- The Castle Chronicle
- Posts
- Demystifying Options: A 0 to 1 Guide about DeFi Options
Demystifying Options: A 0 to 1 Guide about DeFi Options
Castle Research: An Introduction to DeFi Options

Options are one of the most underrated niches within Defi, with unprecedented growth potential. However, many consider options too complicated, and prefer to resort to other alternatives.
The aim of this piece is to provide a 0 to 1 guide on DeFi options, abstracting their complexity and highlighting protocols building in the Options market.


⚔️ A Call to Arms
Think you have what it takes to enter the Castle and contribute to research, community initiatives, due diligence analysis, and advising/servicing projects in the space? Or maybe you want to upskill and shadow community members who have already walked a successful path as an intern?

What are Options?
An options contract gives the buyer the right to buy or sell—depending on the type of contract they hold—the underlying asset.
Unlike futures, the holder is not required to buy or sell the asset if they decide against it.
For taking on the obligation to buy or sell the underlying asset, options buyers pay a premium to the seller.
Options buyers can purchase either a call option or a put option:
A call option gives the buyer the right to buy the underlying asset at a predefined strike price.
A put option gives the buyer the right to sell the underlying asset at a predefined strike price.

While just starting to pick up volume in DeFi, options are widely utilized in tradFi to:
Hedge investments
Speculation
Volatility trading
Combined strategies
Utilize “cheap” leverage
Different types of Options

The two main types of options traded globally are American options and European options.
The distinction between American and European options has nothing to do with geography, only with early exercise.
American options can be exercised at any time between the date of purchase and the expiration date. European options are different from American options in that they can only be exercised at the end of their lives on their expiration date.
Many options on stock indexes are of the European type.
Because the right to exercise early is desirable and has value, an American option typically carries a higher premium than an otherwise identical European option.
Note: Exercising the option before expiration involves accepting the underlying asset (delivery), which differs from simply closing the position.
Options Risk Metrics: The Greeks
The variables that are used to assess risk in the options market are commonly referred to as "the Greeks."
Greeks are used by options traders and portfolio managers to understand how their options investments will behave as prices move, and to hedge their positions accordingly.
Delta (Δ) represents the rate of change between the option's price and a $1 change in the underlying asset's price. In other words, the price sensitivity of the option relative to the underlying.
Theta (Θ) represents the rate of change between the option price and time, or time sensitivity - sometimes known as an option's time decay. Theta indicates the amount an option's price would decrease over time.
Gamma (Γ) represents the rate of change between an option's delta and the underlying asset's price. This is called second-order (second-derivative) price sensitivity.
Vega (V) represents the rate of change between an option's value and the underlying asset's implied volatility. This is the option's sensitivity to volatility. Vega indicates the amount an option's price changes given a 1% change in implied volatility.

Use our referral system to spread the word about the Chronicle!

Options Protocols in DeFi
The DeFi options sector looks incredibly promising in terms of growth for the next cycle.
Options are part of the derivatives basket, arguably the product with the best Product-Market-Fit (PMF) in the crypto industry, along with gambling.
They can be considered "360° derivatives", where traders can create a payout graphic for any scenario (e.g. they can be bearish up to $30,000 BTC and bullish afterward). This is a proven use case in TradFi, where they have high trading volumes.
Currently, DeFi options protocols can be differentiated into four categories:
Protocols utilizing an orderbook
Protocols utilizing an AMM
Protocols providing structured products based on options strategies
Protocols introducing volatility products
The traded notional volume of options platforms is going parabolic, as shown in the following Defillama chart.
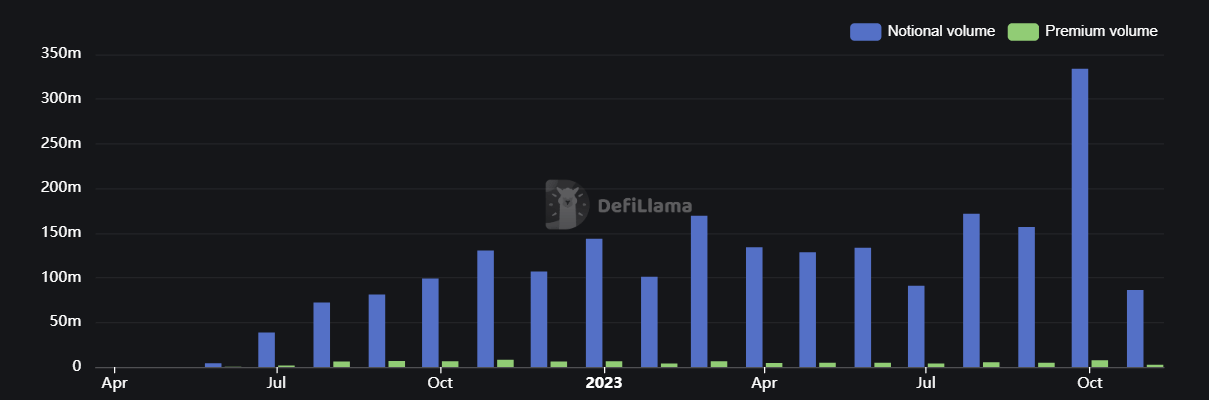
Source: Defillama
However, these are ridiculous numbers compared to CEXs.
CEXs get roughly $40B+ in monthly trading volume for options, while DEXs only get ~$100M in monthly trading volume for options. Almost 40 times less than their centralized competitors.
The majority of options protocols are deployed on two networks:
Optimism (Ethereum Layer 2)
Arbitrum (Ethereum Layer 2)
Note: Some platforms have built their own appchain, such as Aevo, launched by the Ribbon team.
List of options protocols based on Liquidity Model
Orderbook-Based Protocols
•Aevo
•Opyn - Infrastructure
•PsyOptions - Infrastructure
•Lyra finance
AMMs-Based Protocols
•Dopex
•Premia Finance
•Rysk Finance
•Thales Market
•Hegic Options
•Gammaswap Labs
•Panoptic
•Smilee Finance
Structured Products
•Cega
•Jones DAO
•ThetanutsFi
•Ribbon Finance

Overview of options platforms
Aevo
To be a truly fully functioning options exchange, a protocol needs both a futures market and an options market so traders can hedge out their positions.
This is Aevo’s strongest feature.
The exchange runs on a Layer 2 (L2) Ethereum roll-up built on the Optimism (OP) stack. Aevo operates an off-chain orderbook with on-chain settlements.
Before an order is created and posted to the orderbook, it is evaluated through the off-chain risk engine. The risk engine checks margin requirements for that account (either Standard Margin or Portfolio Margin) to determine if it has enough margin to create that order.
Once a maker and taker order gets matched, they get posted on Aevo’s smart contracts, which are deployed on the L2 roll-up.
Aevo uses a custom internal oracle to report the value of the various asset prices to the exchange:
Aevo constructs an Index based on the spot price of various centralized exchanges.
After that, a median of all data sources is calculated, and all pairs that have deviated away from the median by 0.5% are removed.
The final index price is determined by performing a mean of the exchange prices.
Along with the options instruments, Aevo offers its users several perpetual pairs with “exotic” pairs like $FRIEND Index, $TIA Pre-Launch Token, and others, showing their commitment to be on top of the latest market trend.
Lastly, several passive strategies through vaults are available for users interested in investing in options, but with no knowledge about these instruments. This whole range of products is possible as Aevo is a product launched by Ribbon Finance, a structured products provider.

Lyra
Lyra is an option automated market maker (AMM) that allows traders to buy and sell cryptocurrency options against a pool of liquidity.
Traders can either buy or sell options to the Market Maker Vault (MMV) while they pay fees (in the form of the bid-ask spread) to Liquidity Providers (LPs) as compensation for their liquidity.
LPs provide liquidity in an MMV which means they are taking the opposite side of the trade from the platform traders, earning trading fees and premiums as rewards.
A difference from other option protocols is that Lyra uses the Synthetix Protocol on Optimism and GMX on Arbitrum for delta hedging the AMM. In this way, the protocol aims to keep the exposure of liquidity providers close to delta-neutral. For instance, if the AMM is long 500 ETH deltas, it may short 500 deltas with a perpetual to maintain delta-neutral exposure.
The team is working on releasing Lyra v2, a decentralized settlement protocol for spot, perpetual, and options trading built on top of Lyra Chain, a custom-built L2 on the OP Stack.

The new platform will utilize a Central Limit Orderbook (CLOB) to provide users with:
Options
Perpetuals
Spot
Lyra V2 introduces a remarkable feature: “Margin Capabilities”.
The Lyra v2 Risk Engine clears and settles all of the trades on the protocol while supporting:
Portfolio margin for options
Cross-margin between options and perpetuals
Cross collateral
To make it easier, you can sell BTC puts using ETH as collateral, and hedge your position with perpetuals, all in the same protocol.
Premia
Premia is a multi-chain decentralized options market based on a pool-to-peer architecture, a Request for Quotation (RFQ)/Orderbook messaging layer, and automated liquidity vaults.
There are currently three versions of the Premia protocol:
• Premia v1: Peer-to-peer orderbook-based options exchange
Launched early 2021 - Deprecated late 2021
• Premia v2: AMM-based options exchange
Launched late 2021
• Premia v3: Concentrated AMM-based options exchange w/ peer-to-peer order network
Premia V3 was released in early September 2023, as a complete revamp of the original protocol.
This upgrade enables:
Concentrated Liquidity
Partial Collateralization (coming soon)
Vaults & OTC Liquidity
European-style Options
Margin System (planned for the end of Q4)

The biggest change Premia has undergone was the transition to concentrated liquidity, which made them the first on-chain hybrid AMM/Orderbook for options.
Concentrated liquidity enables LPs to maximize fees while improving capital efficiency. Indeed, Premia V3 can be thought of as Uniswap V3 for options.
Range orders can be created by submitting liquidity in a price range that may or may not contain the current option price.
If the range is below the current price → it’s a buy order.
If it is above → it’s a sell order.
This duality enables Premia v3 users to earn fees in automated range orders and trade or market-make in traditional orderbook fashion. Exchange traders will also benefit from increased liquidity and better option pricing.
Rysk
Rysk Finance is a DeFi options protocol on Arbitrum, enabling anyone to trade options with a wide range of strike prices and expiry dates while generating uncorrelated returns for its liquidity providers.

The main focus of Rysk is to offer tight bid and ask spreads for traders, deep concentrated liquidity, and improved capital efficiency.
To deliver these promises, Rysk leverages a Dynamic Hedging Vault (DHV) - a hybrid AMM and RFQ options protocol.
The DHV is the core product of Rysk. It carries out a market-neutral strategy to generate uncorrelated returns for its liquidity providers.
The DHV works by buying and selling options dynamically to maintain a neutral exposure to the market. By doing so, the DHV is able to profit regardless of whether the market goes up or down.
Liquidity providers can deposit their assets into the DHV and earn yields on their deposits, generated from the trading profits of the DHV.
In addition to this, Rysk offers four options trading strategies on the platform:
Call Credit Spread: A bearish strategy that profits if the underlying asset stays below the lower strike price or declines moderately.
Put Credit Spread: A bullish strategy that profits if the underlying asset stays above the higher strike price or rises moderately.
Long Straddle: A neutral strategy that profits if the underlying asset moves significantly in either direction but loses money if it stays within a narrow range.
Long Strangle:
A neutral strategy that profits if the underlying asset moves significantly in either direction but to a lesser extent than a long straddle.
Dopex
Dopex provides users with naked options and options-powered strategies.
They focus a lot of effort into DeFi composability, as Dopex is integrated with multiple protocols:
GMX
Jones DAO
SushiSwap
Silo Finance
Among the products provided by Dopex, we can find Single Staking Option Vaults (SSOV), Option scalps, and Options LPs (OLPs).
The SSOVs allow users to write (sell) or purchase (buy) options like other trading platforms, while option scalps are an innovative way for users to scalp trading through option methodology.

Scalping is a trading strategy that employs short timeframe high leverage positions to maximize exposure to short-term volatility.
The third product, OLPs allow SSOV purchasers to exit positions mid-epoch against a liquidity pool. Dopex SSOVs are European-style options that can only be settled at expiration.
This creates friction for option purchasers who might want to exit their positions early. OLPs also function as a secondary marketplace for option purchasers that might want to sell their positions against a liquidity pool at an IV discount (lower IV equates to cheaper options as per the Black-Scholes Model), allowing them to close their trades mid-epoch.
OLP liquidity is provided by users willing to purchase options mid-epoch at a discount. Those who successfully purchase these options can hold their position until settlement or sell it back into the OLP.
Hegic
Hegic is an on-chain peer-to-pool options trading protocol built on Ethereum. It allows trading of BTC or ETH call and put options with various strategies for hedging, yield generation, leverage, and speculation.
Hegic options are American-style options settled in USDC. Market participants can trade options as a buyer or provide liquidity through the "Stake & Cover pool", a liquidity provision and utilization model.

Token holders can supply $HEGIC into the pool for collateralizing options and option strategies sold through the protocol.
Participants receive 100% of net premiums earned on selling ATM & OTM options and option strategies, with net premiums earned (or losses accrued) distributed proportionally among all pool participants.
Positive PnL is accumulated during the set Epoch period and distributed proportionally among participants in USDC, which can claim it anytime after the end of the Epoch.
The PnL share of USDC linked to users' addresses will not be utilized in the next Epoch if negative. It will instead be covered by HEGIC allocated to the pool.
The HEGIC/USDC conversion rate for covering negative PnL is set based on the previous Epoch's token price performance. This is announced five days before an Epoch starts, to allow users who are not satisfied with the conversion rate to skip the Epoch.
Sharwa Finance is a trading protocol built on Arbitrum, offering margin trading with up to 10x leverage, as well as sophisticated option-based products.
The platform acts as an aggregator of options protocols, routing all orders to other protocols. Hegic, Lyra, and Premia are utilized for options trading, while Uniswap is the counterparty for margin trading.
The value proposition of the platform is in its simple UI/UX and the opportunity for users to purchase option strategies with just one click, leveraging liquidity from multiple option markets and having the flexibility to pay with any asset.

GammaSwap
GammaSwap is an oracle-free DEX for trading volatility (gamma) built on Arbitrum. Their key innovation is in the ability for traders to borrow LP tokens to receive the inverse payoff for impermanent loss (IL), also known as impermanent gain.
GammaSwap can be defined as a two-sided volatility marketplace. Essentially, traders take positions against liquidity providers by going long/short on IL.
Key Takeaways:
No funding rate: Traders pay interest to LPs based on demand for volatility.
No liquidations: Price direction doesn’t affect traders positions. However, positions could get forcibly closed if Loan-to-Value (LTV) gets too low.
No oracles: GammaSwap is built on top of Uniswap and utilizes its pairs and liquidity pools.
What can you do on GammaSwap?
Long (if you expect token prices to change)
Short (if you expect prices to remain steady)
Straddle (neutral strategy, profiting off volatility)

How does Gammaswap works?
Long traders borrow LP positions using their deposits as collateral and break down the pair.
If the total value of the LP tokens is worth 1000 USDC and 0.5 WETH, assuming the price of ETH is $2000 USD, then the position will be rebalanced to 800 USDC and 0.6 WETH respectively. The purpose of the rebalancing is to make the exposure more directional.
This position mimics the returns of a covered call in traditional finance. If the price increases, the trader's PnL increases exponentially and the trader is also protected from liquidation on the downside.
From the LP lender perspective (short traders), they earn the borrowing fees on top of everything they get from the Constant Function Market Maker (CFMM).
In sum:
Short traders (LPers) in CFMMs are betting that trading fees + borrowing interest will outweigh volatility (IL)
Long traders are betting that volatility profit (IL) will outweigh fees + interest.
Smilee
Smilee is an on-chain options protocol known for “Impermanent Gain” options, similar to GammaSwap. Smilee offers users the opportunity to bet and/or hedge against market volatility.
Impermanent Gain buyers earn the IL endured by liquidity providers, and along with leverage, this results in high profits for these buyers.

Smilee operates an AMM to allow users to enter and exit positions at any time with market-driven pricing based on the Black & Scholes model (a differential equation widely used to price options contracts based on the strike price of an option, the current underlying price, the time to expiration, the risk-free rate, and the volatility).
Liquidity deposited on Smilee stays on Smilee — mimicking the behavior of a DEX through a synthetic engine.
Consequently the performance of the liquidity position will be very similarly to a DEX such as Uniswap, with the addition of:
Stablecoin Yields
More reliable Returns (Volatility is less volatile than volume)
Lower IL
Panoptic
Panoptic is an oracle-free perpetual option protocol using Uni V3 LP as their building block for options trading.
Panoptic allows LPs to deposit their liquidity, which is then put in Uniswap V3. As a result, LPs on Panoptic earn trading fees on Uniswap.
Another benefit of using Uni V3 liquidity pools is that traders can buy and sell options relying on the deep liquidity of Uniswap.

Though, the true innovation of Panoptic is “perpetual options”: non-expiring options that can be created by anyone for any asset.
When an option buyer wants to trade on Panoptic, they pay a commission to mint the option and then a streaming option premium (similar to the funding rate in perpetual products). This model allows the platform to not rely on oracles, as the premium is calculated by checking the LP fees that would have been collected if the liquidity remained in Uniswap.
Panoptic rearranges the liquidity to mimic an option payoff. The commission is paid by options buyers and sellers to Panoptic liquidity providers, and these trading fees are considered the options premium.
ThetaNuts
Thetanuts Finance is the premier DeFi structured products protocol for diversified, organic yield generation. The platform is designed to provide treasury management for DAOs and help retail traders earn organic yields on their assets.
The platform is currently in its late v2 stage, with vaults earning yield in the form of premiums as the main product. Each option vault has a predefined delta and tenor designed to create a specific risk-adjusted yield denominated in the deposited asset. After each epoch, the basic vault reinvests the yield generated back into the vault, effectively compounding the yields over time.

The primary objective of these vaults is to sell automated option strategies to generate passive income or accumulate tokens on behalf of users. However, this model comes with three main issues:
Limited Flexibility: Only the sell-side of options is advantageous
Epoch-based systems are not practical: Low capital efficiency
Centralization: Major volumes come from MM, which need a direct negotiation
ThetaNuts is going to release its v3 soon, which will enable users to:
Enter and exit positions anytime
Get long exposure
CEX-like trading experience
More yield opportunities
After the v3 deployment, ThetaNuts is going to release its awaited tokens.
$35M of funds have been raised over the two years to create a good platform for all kinds of users and have a well-planned Token Generation Event (TGE).

Protocols Overview Table


Key takeaways about each liquidity model
Orderbook-based Protocols
Most protocols, including Aevo, have an orderbook that supports only option minting and settlement, with trading done off-chain.

Aevo Daily Volumes: Defillama
Zeta, an option platform on Solana, is the only one with a fully on-chain orderbook at the moment, but it lacks volumes.

Zeta Daily Volumes: Defillama
However, a few protocols are migrating from an AMM model to an orderbook based on.
AMM-based Protocols
Platforms like Dopex, Premia, and Thales only allow users to buy options, but not to sell them back. They employ European options, which must be held until expiration.
On the other hand, Lyra, Hegic, and Rysk allow users to buy and sell options.
The first ones are focused on prioritizing fees-generating volume by option sellers, with a riskier approach (Maximizing liquidity).
The second ones have a more convervative approach: they sell options too, but also hedge to protect themselves and manage risk.
In the current market, AMM-based platforms are generally more efficient than those based on orderbooks.
But there is a drawback for LPs, as they can't choose which options to sell, and if they want to exit, they might face IL.
Volatility Products
Protocols such as Gammaswap, Smilee, and Panoptic are based on AMMs but have different mechanisms.
These platforms utilize popular AMMs like Uniswap to provide deep liquidity to their products instead of relying on their one AMM.
Nonetheless, they have different scopes; while Panoptic provides “perpetual options”, GammaSwap and Smilee allow users that provide LP on external AMMs to hedge against IL (Impermanent Loss) by trading volatility.
That’s a different type of product, which is receiving good feedback from the market.
Structured product providers
ThetaNuts, Ribbon, and Cega offer users yield vaults based on options strategies.
DeFi Option Vaults(DOVs) essentially simplify the experience for users by allowing them to deposit & earn yields from automated option strategies.
The two most used are:
Covered call - Hold a long position and sell call options (Bullish)
Put selling - Sell put options without shorting (Bearish)
These protocols have demonstrated PMF as they simplify options trading for retail users who lack experience in the topic.
This can be confirmed also by the recent funding rounds made by ThetanutsFi ($18M) and Cega ($9.3M) this year.
Furthermore, these types of projects tend to perform really well during high volatility periods, as there’s a need for hedging against downside risk, and market makers are willing to pay higher premiums. On the other side, during low volatility periods, there isn’t a high demand for these strategies, and these platforms tend to lose TVL and volumes, as happened in the last year.

Volume, TVL, and Capital Efficiency - How to Evaluate Options Protocols.
The TVL is the most used metric to analyze DeFi protocols, as it indicates the amount of money stored in a specific platform. However, when it comes to options and derivatives, this metric provides only half of the picture.
In the specific case of orderbooks, TVL is not a great metric, as there is no liquidity pool of assets waiting for a transaction to occur. In options, the TVL would equal to the collateralized liquidity + options premiums waiting to be distributed to the sellers.
Furthermore, in options the TVL is not only used as collateral but also as available liquidity.
Recognizing that TVL represents liquidity, we can find more insightful ways to assess the "capital efficiency" of these platforms. For instance, this can be done through the volume-to-TVL ratio that examines the relationship between the trading volume and the TVL.
Why is this important?
It allows us to compare the trading volumes, taking into account how much liquidity is sitting in the protocols. In this way, it’s possible to interpret how much trading volume $1 in liquidity facilitates over seven days.
Another question we should be asking is: How much of the trade volumes of token-based protocols were incentivized?
For example, on Lyra, users were offered both LYRA and OP rewards. At the end of these incentives, there was a shift in user behavior, resulting in a decline in trading activities on Lyra. Similarly, trading on Premia decreased when the ARB airdrop occurred.
Collateralization, Hedging, and Liquidations.
DeFi options initially required full collateralization but evolved to enable partial collateralization or borrowing capital for trading, allowing reduced upfront capital in exchange for higher risk.
The introduction of margin and liquidations in options trading protocols can offer users greater flexibility and potentially higher returns, but it also comes with additional risks and complexity:
Users need to manage their collateral and margin levels carefully to avoid liquidation.
Protocol creators must design and implement margin and liquidation processes to ensure the stability and security of the protocol.
The next step was to put the collateralizing capital to work. While collateral is typically used for hedging, it can also be used to generate additional returns or reduce losses by lending it through an overcollateralized protocol.
In TradFi this is called “Working Collateral”.
The use of working collateral is common in TradFi, but few DeFi protocols adopt this approach due to the associated risks.
Protocols must weigh the risk of redeploying the capital, for example, on other DeFi protocols such as AAVE and Compound, against potential risks such as having a high utilization rate, collateral that cannot be redeemed, or a third-party protocol that is compromised.
Beyond the lack of low-risk highly liquid investments, adding working collateral to DeFi protocols can make deposits and withdrawals more gas-intensive for users, given the need to convert and/or stake assets. Additionally, assuming protocols let users deposit and withdraw during a 24-hour window, it would imply they need to track all staking operations to have proper accountability.
For instance, if two users deposit at different times within a 24-hour period, they may not be entitled to the same yield depending on when they deposited.
Now onto hedging strategies, which aim to mitigate risks related to market exposure.
Liquidity provision in AMMs involves passively providing liquidity to a market by buying and selling options at any time. On the one hand, this is great for users, since there’s always liquidity available to buy or sell the options. On the other hand, this creates inventory risk, which can arise if the price of the assets moves against the AMM and results in losses for the liquidity pools.
To manage this risk, AMMs typically hedge their positions through delta hedging, which involves holding additional assets, option contracts, or using perpetual futures to offset their exposure.
Suppose there's a significant amount of call options in a given position. To prevent potential losses due to price fluctuations, one possibility is to add a small put-option position as an offset. Another strategy might be to sell a carefully chosen number of call options at a different strike price.
Nonetheless, hedging options can have their own risks, such as the possibility of losing the hedge and not being protected against losses. Additionally, the capital used for hedging reduces the liquidity available for trading and assumes that the losses reduced by hedging are greater than the fees generated from said liquidity.
In conclusion, options trading protocols must carefully consider their margin requirements and liquidation processes to provide a stable and user-friendly trading environment for users while weighing the risks and benefits of working collateral and collateral hedging.
Why are option protocols not growing at the same pace as perpetuals?
Since the market realized perpetual protocols were necessary following the collapse of the FTX, the industry has experienced enormous growth. This is not the case for options products, which have had less remarkable growth over the past months.
Setting aside the fact that perpetual instruments have been introduced much earlier compared to options which partially explains the difference in growth and adoption between the two sectors, there are several issues that options face before going mainstream:
• Low liquidity and fragmented pools make it difficult to execute large trades.
• There are not enough traders to offer economic incentives to LPs and attract liquidity to the market.
• Options trading requires a high level of liquidity for efficient price discovery.
We are already witnessing innovative solutions being built around these problems.
Nonetheless, some may argue that even after solving the above issues, options in Defi may still struggle to get adoption, due to users being more familiar and preferring perpetual markets rather than option ones.
Traders do like perpetuals, as they don’t require any upfront payment unlike options (premium upfront), and are an easier instrument to understand.
How could the sector evolve in the next months?

The BTC Spot ETF approval could be a double catalyst for the options sector.
From a generic perspective, the ETF is going to bring market volatility back, which will lead to more demand for options in general from market makers. MMs tend to use both CEX and Decentralized Options marketplace to hedge against their positions.
In low volatility periods, there's no need to hedge for MMs, so they tend to low-ball the options premiums, discouraging retail users to take the sell-side counterparty to the MMs (options buyers).
More volatility = more need to hedge (higher demand) = better options premium pricing = better yields for options underwriters / DOVs (Options LP) = growing options markets.
The second “catalyst” would be that options would start to get used more and more as in TradFi, where they are a tool to hedge and/or speculate on ETFs.
With the potential growth of the sector, along with the general market, we could see projects providing structured products building new blocks for DeFi options composability.
New projects such as GammaSwap, Panoptic, and Smilee Finance are introducing simple products and an easier UX, to attract new users and simplify the complexity of options.
Furthermore, these protocols may result attractive as none of them has released a token yet and users will be incentivized to test them as they get closer to TGE.
Furthermore, “special” attention should be given to these five projects that have received a grant from the Arbitrum Foundation and could see an increase in volumes and TVL with the upcoming incentives they will deploy:
Tally
Rysk Finance
Premia Finance
Dopex
Jones DAO

This research has been brought to you by Mooms.

Thanks for reading, please give us a follow on Twitter at @Castle__Cap and visit our website to learn more about our services and get in touch.
Virtually yours,
The Castle

The Alpha Assembly
Receive Telegram notifications of our posts and those of our partners! Join the Alpha Assembly Telegram channel today!
The central hub for everything crypto:
High-level on-chain capital movements
Web3 gaming insights
DeFi research and strategies to give you an edge
Covering everything NFT related: collections, tools, NFT-fi, you name it
News, alpha, and on-the-pulse-content

Reply